Dr. Kevin Lam* Dr. Wesley Drew Chapman * Dr. Isin Mustafa
Dr. Patrick Bartholomew * Dr. Lauren Pelucacci * Dr. Sahiba Singh
Dr. Joseph Altepeter * Dr. Lori DeBlasi * Dr. Robert Bello
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis. It is fairly common condition that is very painful. It usually attacks one joint, more commonly the big toe. It may also be found in other joints such as the hand, wrist, elbow, knee, and ankle.
Symptoms in the affected joint/s may include
• Intense pain in one or more joints
• Swelling in and around the affected joint
• Red, shiny skin over the affected joint
• Heat and tenderness in the joint
• Limited range of motion in more advanced cases
There are times when the symptoms get worse, which is known as gout flares while there are times that there are no symptoms. If gout remains uncontrolled, there may be repeated bouts that can lead to gouty arthritis, a worsening form of arthritis.
Gout is caused by a condition known as hyperuricemia, which happens when there is too much uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a breakdown product of purines from the food we eat. The crystallization of uric acid in the joints cause the pain attacks and may lead to kidney stones as well.
Gout symptoms may come and go but there are some ways to manage symptoms and prevent gout flares. Maintaining adequate fluid intake may help curb attacks. Dietary changes such as avoiding purine rich foods may also help.
Certain medications may reduce the pain and inflammation of gout attacks. These include NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids. Other drugs work to decrease the level of uric acid in the blood and prevent uric acid deposits in the joints such as allopurinol, probenecid, febuxostat, and lesinurad. Newer drugs are being developed to manage chronic gout.
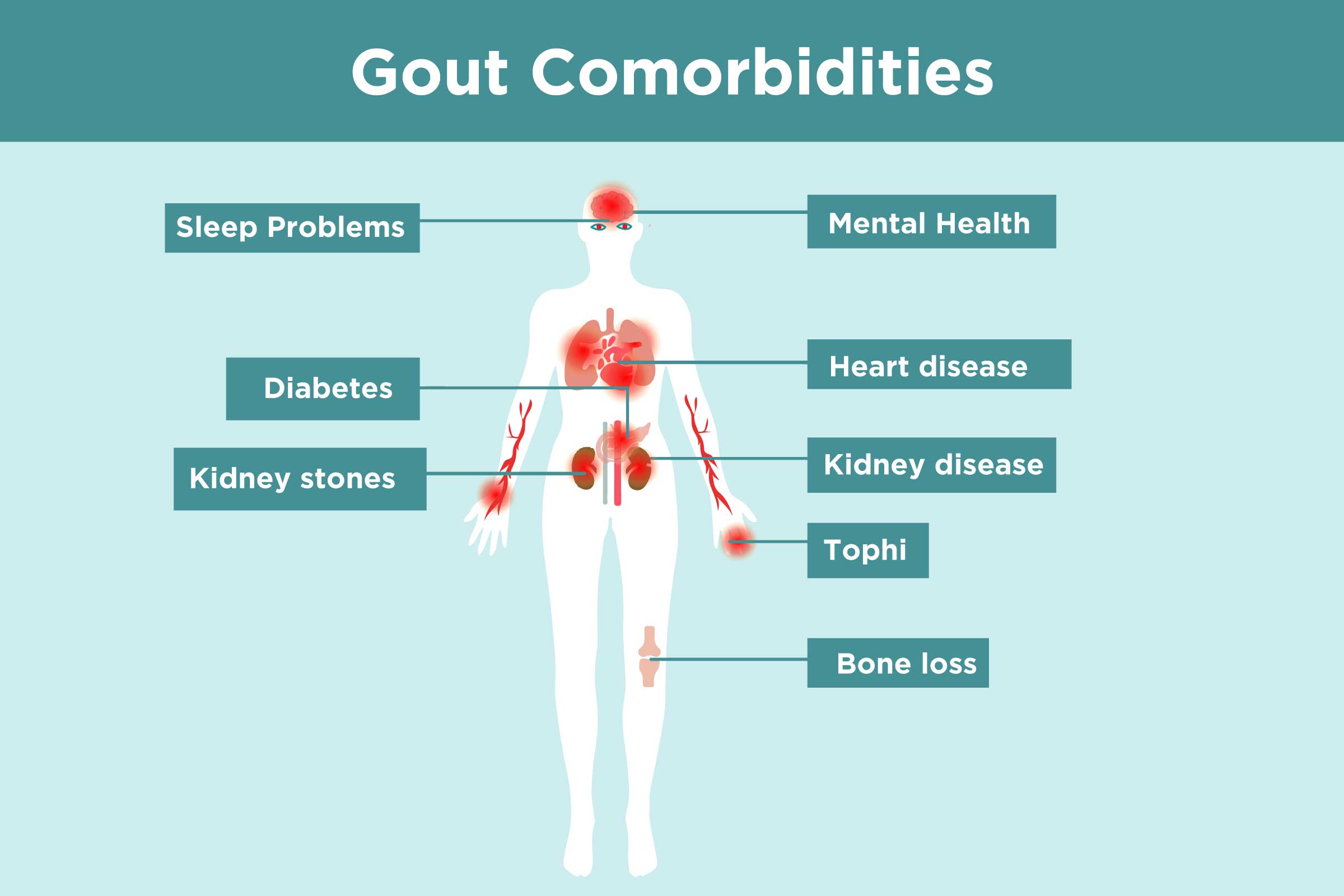
If you experience sudden and intense pain in your joint, seek medical care as soon as possible. Untreated gout can lead to worsening pain and joint damage. Gout comorbidities include sleep problems, mental health problems, diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, tophi, and bone loss.
If you have chronic gout, contact us to find out more information.

We have 9 convenient locations throughout Collier, Lee, Charlotte, and Sarasota Counties
Copyright FLPODIATRIST